Honda Motor Co. has announced significant changes to its operations in China, including the closure of a manufacturing plant, as the Japanese automaker grapples with declining sales and intensifying competition in the world’s largest automotive market.
Plant Closure and Production Halt
Honda will close a plant operated through its joint venture with Chinese state-owned automaker Guangzhou Automobile Group (GAC) in October 2024. This facility, which has been in operation for nearly two decades, has an annual production capacity of 50,000 vehicles and has been manufacturing the Accord sedan model.
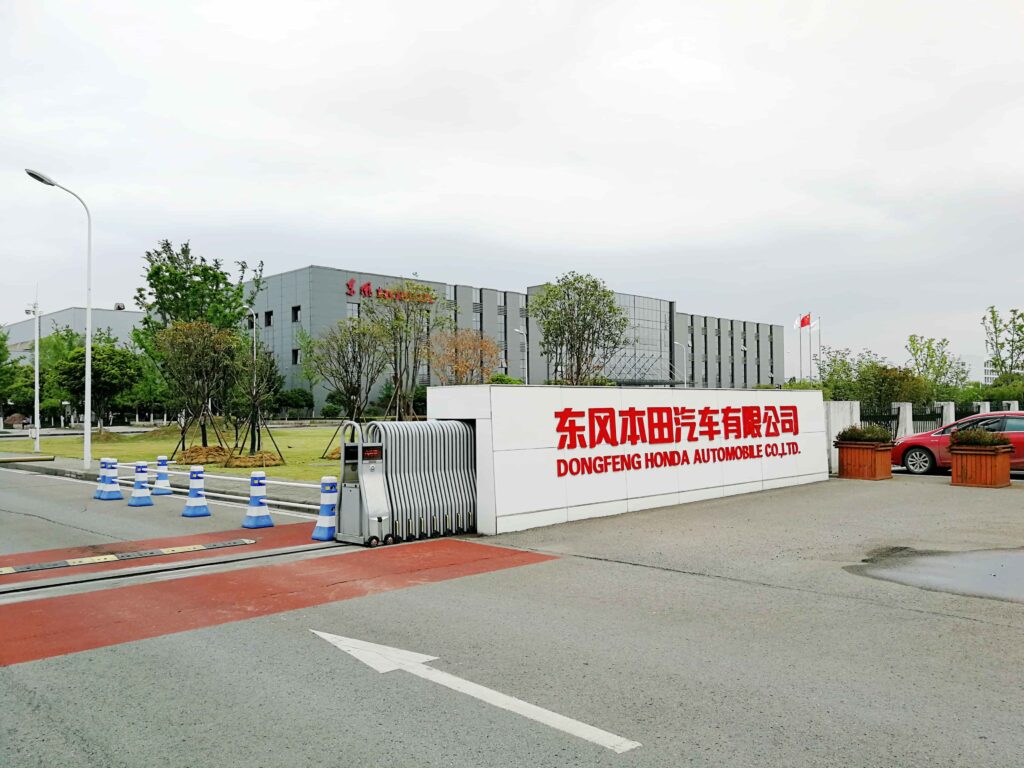
In addition to the plant closure, Honda will pause production at another factory in China, operated through a separate joint venture with Dongfeng, starting from November. This facility has an annual production capacity of 240,000 vehicles.
Reduction in Production Capacity
As a result of these changes, Honda’s annual production capacity in China will decrease from 1.49 million to 1.2 million vehicles. This represents a significant reduction of approximately 290,000 units, primarily affecting gasoline-powered vehicles. The move marks Honda’s first-ever cut in production capacity in China, which has served as the automaker’s largest production base.
Shift Towards Electric Vehicles
While reducing its gasoline vehicle production, Honda is simultaneously increasing its focus on electric vehicles (EVs) in the Chinese market. The company plans to start production at two new EV plants later this year, which it is building through its joint ventures with GAC and Dongfeng. These new facilities are expected to add 240,000 units to Honda’s annual production capacity, bringing the total back up to 1.44 million vehicles.
Market Challenges
The decision to reduce production capacity comes amid challenging market conditions for Japanese automakers in China. Sales of Japanese automobiles have been declining, partly due to intense price competition and the rapid rise of Chinese domestic brands, particularly in the EV segment.
Honda is not alone in facing these challenges. Other Japanese automakers, such as Nissan Motor Co. and Mitsubishi Motors Corp., have also been forced to make similar adjustments to their Chinese operations.
Broader Industry Impact
The struggles of Japanese automakers in China are having ripple effects beyond the automotive sector. For instance, Nippon Steel Corp. recently announced plans to dissolve its joint venture with Chinese steelmaker Baoshan Iron & Steel Co., citing slumping sales of Japanese cars in China as a factor.
As Honda and other Japanese automakers navigate these challenging market conditions, they are likely to continue adjusting their strategies and operations in China. The focus on increasing EV production while reducing gasoline vehicle capacity reflects the broader industry shift towards electrification, particularly in the highly competitive Chinese market.